Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. It’s not just individuals with diabetes who need to be mindful of their blood sugar; this is a fundamental aspect of health that affects everyone. Proper blood sugar regulation can help prevent serious health issues such as diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic disorders.
Why Manage Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar levels dictate a lot about how we feel each day. When levels spike or drop significantly, it can lead to energy crashes, irritability, and makes it harder for the body to perform its essential functions. Over time, consistently high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as vision impairment, kidney disease, and even stroke.
Natural Methods and Lifestyle Changes
There are effective, natural ways to manage blood sugar that can complement medical treatments or provide a foundation for good health:

- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and proteins while limiting sugars and refined carbohydrates helps maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps the body regulate blood sugar naturally by increasing insulin sensitivity, which allows the muscles to use glucose more effectively during and after activity.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular relaxation can help prevent the blood sugar spikes that stress hormones like cortisol can cause.
By adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to manage blood sugar effectively, leading to better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, scientifically known as glucose levels, are a critical measure of how well our body processes energy from food. The understanding of these levels is fundamental for managing overall health, especially for individuals dealing with conditions like diabetes.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels?
Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in your blood at any given time. Glucose is the main source of energy for your body’s cells and is obtained through the food you eat. The body regulates these levels with the help of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, which helps glucose enter the cells.
Impact on the Body
Properly balanced blood sugar levels ensure that your body’s systems function optimally. When these levels are too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia), it can lead to various health issues:
- High Blood Sugar: Can cause symptoms like frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and over time, can lead to severe complications such as kidney damage, nerve problems, and cardiovascular disease.
- Low Blood Sugar: Can cause immediate symptoms such as shaking, sweating, rapid heartbeat, hunger, and severe confusion; it can be dangerous and needs to be treated promptly to prevent more serious effects like loss of consciousness.
Common Triggers of Blood Sugar Spikes
Several factors can cause blood sugar levels to spike, including:
- Diet: Consuming high amounts of sugars or simple carbohydrates can quickly elevate blood sugar.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Physical activity helps the body regulate blood sugar levels; inactivity can impair this regulation.
- Stress: Stress can trigger the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar.
- Illness: The body produces hormones to fight illness which may also raise blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with abnormal blood sugar levels is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include fatigue, headache, difficulty concentrating, and changes in vision. Regular monitoring of blood sugar, especially for those at risk of or managing diabetes, is essential for maintaining good health.
Benefits of Gum Arabic for Blood Sugar Management
Gum Arabic, also known as acacia gum, is a natural gum harvested from the sap of acacia trees. Its unique properties and health benefits make it an excellent dietary supplement, particularly for managing blood sugar levels.
Health Properties of Gum Arabic
Gum Arabic is rich in soluble fiber, which helps to regulate digestion and slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. This slow absorption is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar more effectively.
Role in Blood Sugar Management
The soluble fiber in Gum Arabic has a prebiotic effect, fostering healthy gut bacteria, which plays a role in inflammation and glucose metabolism. By improving gut health, it indirectly supports better insulin sensitivity and glucose management. Clinical studies have shown that regular intake of Gum Arabic can help reduce blood glucose spikes after meals, which is critical for preventing long-term complications of diabetes.

How to Use Gum Arabic for Maximum Benefits
To harness the full potential of Gum Arabic for blood sugar management:
- Preparation: Dissolve one tablespoon of Gum Arabic powder in a glass of lukewarm water.
- Timing: Drink this mixture about 30 minutes before meals. The timing helps to prepare the digestive system to process incoming food more steadily, smoothing out potential blood sugar spikes.
- Consistency: For best results, incorporate this practice into your daily routine, aligning it with your main meals to maintain consistent blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Including Gum Arabic in your diet is not only beneficial for blood sugar management but also contributes to overall digestive health, which is intrinsically linked to broader metabolic functions. As with any supplement, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it fits within your overall health strategy, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medication.
Dietary Changes for Blood Sugar Control
Managing blood sugar levels effectively requires careful attention to your diet. What you eat has a direct impact on your blood glucose levels, and making informed dietary choices is key to maintaining balance. Here’s a guide on what foods to include and avoid to help stabilize your blood sugar.
Foods to Include for Stabilizing Blood Sugar
- Whole Grains: Unlike refined grains, whole grains have a lower glycemic index and provide more fiber, which slows down the absorption of glucose. Examples include quinoa, barley, and whole wheat.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are low in calories and carbohydrates, which means they have little impact on blood sugar.
- Nuts and Seeds: These are good sources of fiber and healthy fats, helping to moderate blood sugar rises after meals.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in fiber and protein, making them excellent for blood sugar management.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can improve heart health and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Foods to Avoid to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes
- Sugary Beverages: Soda, fruit juices, and other sugary drinks can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, and rice are high glycemic foods that can quickly raise blood sugar levels.
- Pastries and Sweets: Cookies, cakes, and other desserts are not only rich in sugar but also fats, which can lead to weight gain and affect insulin sensitivity.
- Fried and Greasy Foods: These can contribute to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes and worsen blood sugar control.
- High-Fat Dairy Products: Some studies suggest that certain high-fat dairy products might worsen insulin resistance.
By incorporating these dietary recommendations into your daily routine, you can better manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of diabetes-related complications. Consistency is key, and making gradual changes can help you sustain these healthier eating habits long-term.
The Role of Hydration in Blood Sugar Management
Staying adequately hydrated is a crucial but often overlooked aspect of managing blood sugar levels. Hydration influences various bodily functions, including how your body regulates glucose levels.
Impact of Hydration on Blood Sugar Levels
1. Enhances Kidney Function: Proper hydration helps the kidneys to efficiently process blood and filter out excess glucose through urine. Dehydration can cause the kidneys to struggle in processing blood sugar effectively.

2. Affects Blood Sugar Concentration: When you’re dehydrated, your blood volume decreases, leading to a higher concentration of blood sugar. Keeping hydrated helps maintain your blood volume and dilute your blood sugar concentration.
3. Supports Metabolic Function: Water is essential for metabolic processes, including the breakdown of carbohydrates and the release of energy. Adequate hydration ensures these processes are efficient and can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Tips for Incorporating More Fluids Into Your Daily Routine
1. Start Your Day with Water: Begin your morning with a glass of water to kickstart hydration after the night’s fast.
2. Infuse Your Water: If you find plain water unappealing, add slices of fruits like lemon, lime, or cucumber to enhance the flavor without adding significant calories or sugar.
3. Use a Water Bottle: Keep a water bottle handy throughout the day as a constant reminder to drink. Choose a bottle with measurements to track your intake.
4. Drink Before Meals: Having a glass of water before meals can prevent overeating and help manage blood sugar by promoting a feeling of fullness.
5. Choose Hydrating Foods: Incorporate fruits and vegetables with high water content into your diet, such as watermelon, cucumbers, oranges, and celery.
6. Monitor Your Urine Color: Your urine color can be an indicator of hydration levels. Aim for a light yellow color; dark urine may suggest you need more fluids.
By understanding the vital role of hydration in blood sugar management and implementing these practical tips to increase your fluid intake, you can better control your glucose levels and improve your overall health.
Exercise and Blood Sugar Management
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of healthy blood sugar management. Engaging in physical activity not only helps lower blood sugar levels immediately but also improves insulin sensitivity over time, making your body better at using the available insulin to absorb glucose during and after activity.
Types of Exercise Beneficial for Blood Sugar Management
1. Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, swimming, and cycling increase heart rate and breathing, which help improve cardiovascular health and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
2. Resistance Training: Weight lifting, bodyweight exercises, and resistance band workouts help build muscle mass. More muscle means your body has a bigger reservoir to absorb glucose, which can help lower and stabilize blood sugar levels.
3. Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Yoga and Pilates not only improve flexibility and balance but also reduce stress levels, which can help control cortisol and, consequently, blood sugar levels.
Safely Incorporating Exercise into Your Routine
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Check your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise to learn how your body reacts to different activities. This is especially important if you use insulin or are on other glucose-lowering medications to avoid hypoglycemia.
2. Stay Hydrated: Keep yourself well-hydrated during exercise because dehydration can cause blood sugar levels to concentrate and potentially rise.
3. Eat a Balanced Snack: If your blood sugar levels are trending lower before starting exercise, have a small carbohydrate-rich snack to help prevent hypoglycemia during your workout.
4. Wear Proper Footwear: Particularly for people with diabetes, proper footwear is crucial to avoid injuries and infections, especially if peripheral neuropathy is present.
5. Gradual Progression: If you are new to exercise or have not been active for a while, start slow and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. This can help your body adjust without overwhelming your metabolic system.
By incorporating these types of exercises into your routine and following safety guidelines, you can significantly enhance your ability to manage blood sugar levels, leading to better overall health and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
Stress and Its Impact on Blood Sugar
Stress plays a significant role in blood sugar management, and understanding this connection is crucial for anyone looking to maintain stable glucose levels, particularly those with diabetes or pre-diabetic conditions.
Understanding the Connection
Stress, whether physical or emotional, triggers the release of various hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are designed to prepare the body for a “fight or flight” response by increasing blood sugar levels to provide immediate energy to the muscles. While this is beneficial in acute scenarios, chronic stress can lead to persistently high blood sugar levels, which can complicate diabetes management and increase the risk of diabetes-related complications.

Stress-Reduction Techniques
Managing stress is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Here are some effective stress-reduction techniques:
1. Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness or engaging in meditation can significantly reduce mental stress and, consequently, help in managing blood sugar levels. Techniques like guided imagery, progressive relaxation, or simply practicing mindful breathing can center your thoughts and lower stress hormone levels.
2. Regular Exercise: Physical activity is not only good for your physical health but also for your mental health. Activities like walking, cycling, or team sports can reduce stress and improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get enough sleep each night can help regulate the hormones that influence blood sugar levels. Establish a regular sleep routine to improve both sleep quality and stress levels.
4. Yoga: Yoga combines physical poses with breathing exercises and meditation to reduce stress. Its beneficial effects on stress and overall well-being make it a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels.
5. Professional Support: Sometimes, it might be helpful to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor who can provide strategies to manage stress effectively.
By incorporating these stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, you can better manage your stress and, in turn, help maintain more stable blood sugar levels. Managing stress is not only crucial for your mental health but also for effective diabetes management.
Monitoring and Testing Your Blood Sugar
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for anyone managing diabetes or concerned about their blood sugar balance. With the right tools and techniques, you can easily keep track of your glucose levels at home, which is essential for maintaining optimal health.
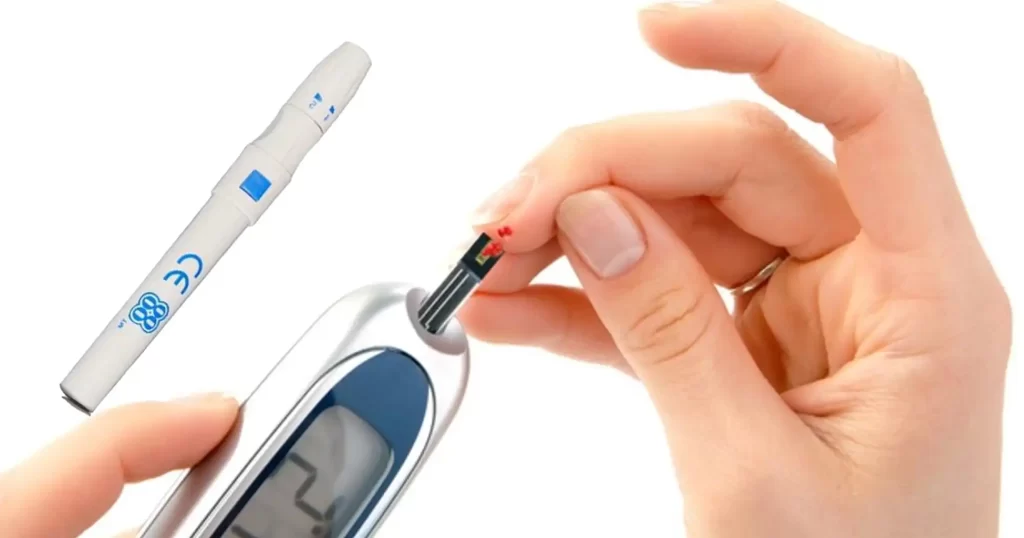
Tools for Monitoring Blood Sugar
- Glucometer: A traditional glucometer is a portable device that measures blood sugar levels from a small drop of blood, typically taken from your fingertip. This method provides immediate feedback on your glucose levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM): CGMs provide real-time, dynamic glucose information, allowing you to see your blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. This device tracks glucose levels via a small sensor inserted under your skin, usually on the abdomen or arm.
- Test Strips and Lancets: Used with a glucometer, test strips and a lancet are essential for traditional blood glucose monitoring. The lancet is a small needle used to prick the finger to obtain a blood sample.
Techniques for Effective Monitoring
- Consistent Timing: Monitoring your blood sugar at the same times each day, such as before meals and at bedtime, can help you understand how your meals and activities affect your glucose levels.
- Record Keeping: Keeping a log of your readings along with notes on your diet, exercise, and any symptoms can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your diabetes management plan.
How Often to Check
- Type 1 Diabetes: If you have Type 1 diabetes, you might need to check your blood sugar more frequently, often four to ten times a day, depending on your insulin treatment.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Those with Type 2 diabetes should follow the monitoring frequency recommended by their healthcare provider, which may vary based on whether you’re using insulin or other management strategies.
- Gestational Diabetes: Pregnant women with gestational diabetes will likely need to monitor their blood sugar several times a day, as directed by their healthcare provider.
What Patterns to Look For
Look for patterns in your blood sugar readings over time. This can help identify potential triggers for high or low blood sugar levels, such as certain foods, activities, or times of day. Understanding these patterns is key to adjusting your diet, exercise, and medication to better manage your condition.
Regular monitoring is a powerful tool in managing diabetes effectively. It not only helps prevent the complications associated with high and low blood sugar but also empowers you to take active control of your health.
Medicinal Interventions for Blood Sugar Management
While natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for managing blood sugar, they may not always be sufficient, especially for individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes. Understanding when to seek medical intervention and the options available is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Recognizing the Need for Medical Intervention
1. Consistent High Blood Sugar Levels: If despite lifestyle changes, your blood sugar levels remain consistently high, it might indicate the need for medication to help control glucose levels.
2. Symptoms of Uncontrolled Diabetes: Experiencing symptoms such as frequent urination, extreme thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, or unexplained weight loss suggests that your current management strategy might be inadequate.
3. Risk of Complications: The presence of diabetes-related health issues like neuropathy, retinopathy, or cardiovascular disease can necessitate more aggressive treatment approaches.
Common Medications and Treatments
1. Metformin: One of the most commonly prescribed medications for type 2 diabetes, metformin improves glucose tolerance and lowers both basal and postprandial plasma glucose.
2. Insulin Therapy: For individuals whose bodies produce little or no insulin (as in type 1 diabetes) or those with severe type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential. It involves administering insulin through injections or a pump to manage blood sugar levels.
3. Sulfonylureas: These medications help your body secrete more insulin. Examples include glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride.
4. DPP-4 Inhibitors: Drugs like sitagliptin and saxagliptin work by affecting the incretin system, which increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in the blood.
5. SGLT2 Inhibitors: This newer class of medications, including canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, works by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the blood, thus lowering blood sugar levels.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best medication strategy for your specific condition. They can provide guidance based on your overall health, blood sugar patterns, and other individual factors.
Medicinal interventions can significantly improve quality of life and prevent complications in those with diabetes. It’s important to approach medication as a complement to, not a replacement for, lifestyle management strategies.
Success Story: Emily’s Journey with Gum Arabic for Blood Sugar Management
Emily, a 54-year-old high school teacher, faced a significant challenge when she was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Determined to manage her condition without relying solely on medication, she began researching natural supplements that could complement her dietary changes and exercise routine. That’s when she discovered the benefits of gum arabic.
Discovering Gum Arabic
After reading about the potential of gum arabic to aid in blood sugar management, Emily was eager to try it. Gum arabic, known for its high soluble fiber content, appealed to her because of its minimal taste and ease of incorporation into her diet.
Incorporating Gum Arabic Into Her Routine
Emily started by adding a tablespoon of gum arabic powder to a glass of lukewarm water every morning, 30 minutes before breakfast. She also took another tablespoon before going to bed. This routine was recommended to maximize the effects of gum arabic in stabilizing blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
Notable Changes and Results
Within a few weeks, Emily noticed significant improvements. Her blood sugar levels, which used to spike after meals, began to stabilize. She felt more energetic throughout the day and experienced fewer cravings for unhealthy snacks. Encouraged by these positive changes, she maintained her routine diligently.
Ongoing Success
Six months into her new regimen, Emily’s HbA1c levels—a measure of long-term blood glucose control—had dropped significantly, surprising her doctor who was monitoring her diabetes. Her success with gum arabic, alongside her commitment to a healthy diet and regular exercise, allowed her to manage her diabetes effectively without increasing her medication.
Emily’s story is a testament to the power of natural supplements like gum arabic in managing health conditions such as diabetes. It highlights how integrating simple, natural products into one’s daily routine can make a significant difference in controlling blood sugar levels and improving overall health.
Her journey continues to inspire others in her community to explore natural remedies as part of their health management strategies, demonstrating that with the right approach and consistent effort, it is possible to live a healthy life, even with diabetes.
Conclusion: Embracing Effective Strategies for Blood Sugar Management
As we conclude this exploration of blood sugar management, it’s important to reflect on the key strategies discussed and their potential to enhance your health. Managing blood sugar effectively is not only crucial for individuals with diabetes but also for anyone interested in maintaining optimal health and preventing future metabolic issues.

Key Takeaways
- Understanding Blood Sugar Levels: Recognizing how blood sugar levels affect the body and the importance of maintaining them within a healthy range is the foundation of good health.
- Natural Remedies and Supplements: Utilizing natural supplements like gum arabic can complement dietary efforts to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating whole foods that stabilize blood sugar and avoiding those that cause spikes is crucial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels.
- Hydration: Keeping well-hydrated assists in regulating blood sugar and supports overall metabolic health.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or simple relaxation exercises can prevent stress-induced spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of your blood sugar levels with appropriate tools helps in making informed decisions about your health.
Moving Forward
We encourage you to adopt these strategies and make them a part of your daily routine. By doing so, you can take proactive steps towards not only managing your blood sugar levels but also improving your overall quality of life. Remember, consistency is key in seeing the benefits of any health regimen.
As you implement these changes, keep in mind that small, consistent adjustments can lead to significant health improvements over time. Whether you’re managing diabetes or simply focused on preventive health, these strategies provide a robust foundation for maintaining lifelong wellness.
Ressources
American Diabetes Association (ADA)
- Provides comprehensive information on all aspects of diabetes care, including blood sugar management, diet, and exercise.
- Visit ADA’s Website
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Diabetes Home
- Offers detailed guides on managing diabetes, including tips on monitoring blood sugar and preventing diabetes-related complications.
- Visit CDC’s Diabetes Section
Mayo Clinic – Diabetes Management
- Extensive articles on how to manage your blood sugar through lifestyle adjustments and medication.
- Explore Mayo Clinic’s Diabetes Management Advice
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- Provides research and education on diabetes, including methods to control blood sugar and prevent diabetes complications.
- Visit NIDDK
Harvard Health Publishing – Managing Blood Sugar
- Offers articles and blogs from medical professionals on the latest research and practical tips for blood sugar management.
- Read Harvard Health on Managing Blood Sugar


3 thoughts on “Crack the Secrets to Balanced Blood Sugar with Simple Lifestyle Changes”